History
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1819
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1819

Foundation of the «Mechanical Workshop Jacob Kern» in Aarau, Switzerland.
1820
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1820
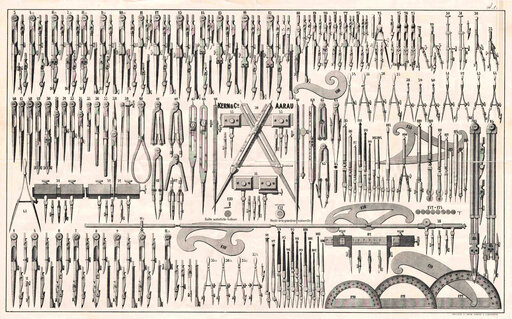
In his workshop Jakob Kern initially produces instruments for technical drawings, for example compasses. Until 1900 they remain the main production branch of Kern and become the worldwide standard for technology and quality.
1835
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1835
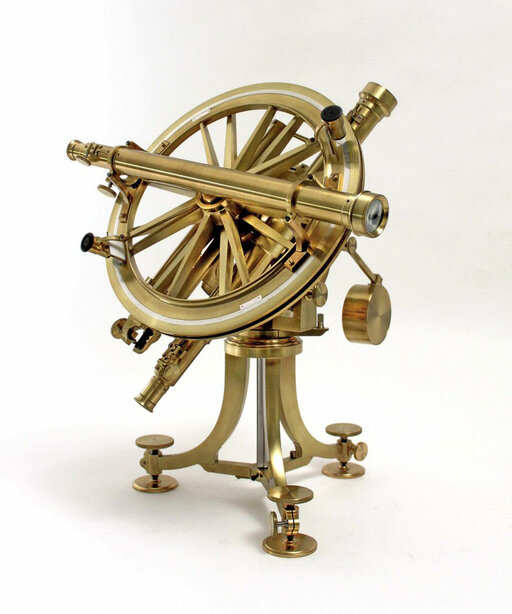

Delivery of a Borda circle, a twelve inch theodolite, to General Dufour. It was an essential tool in the creation of the Dufour map of Switzerland.
1851
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1851

Jakob Kern is awarded at the world exhibition in London for the quality of his products.
1857
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1857
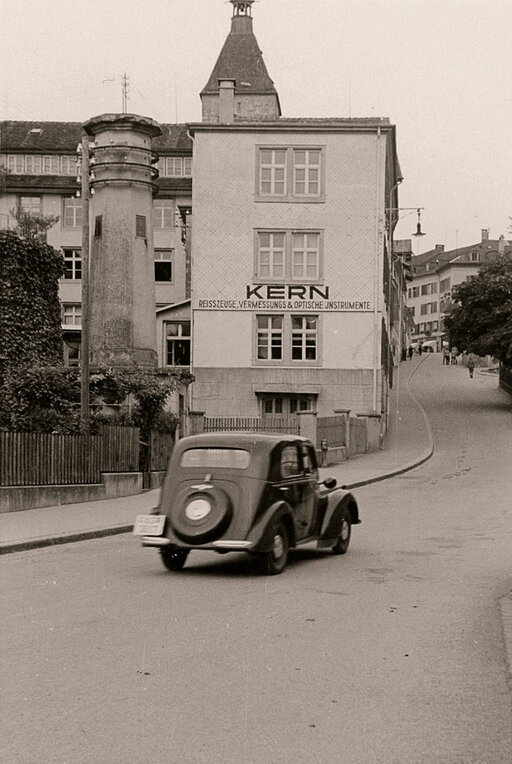

Move into the newly built factory building on Ziegelrain in Aarau.
1869
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1869

Foundation of a company health insurance fund joined by all 115 employees.
1871
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1871
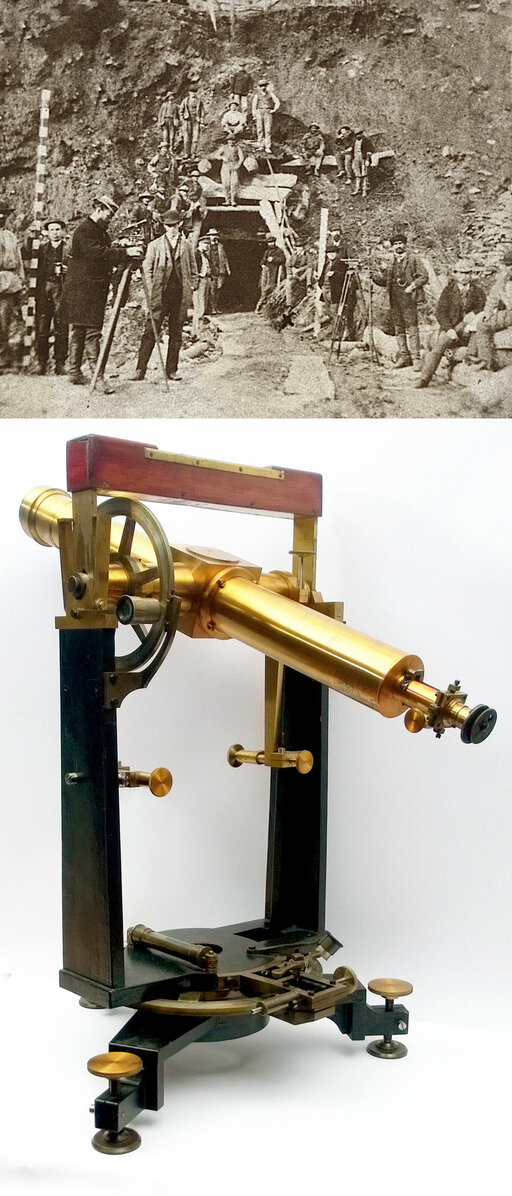

A surveying tool revised and improved by Kern is used in the construction of the Gotthard tunnel.
1898
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1898
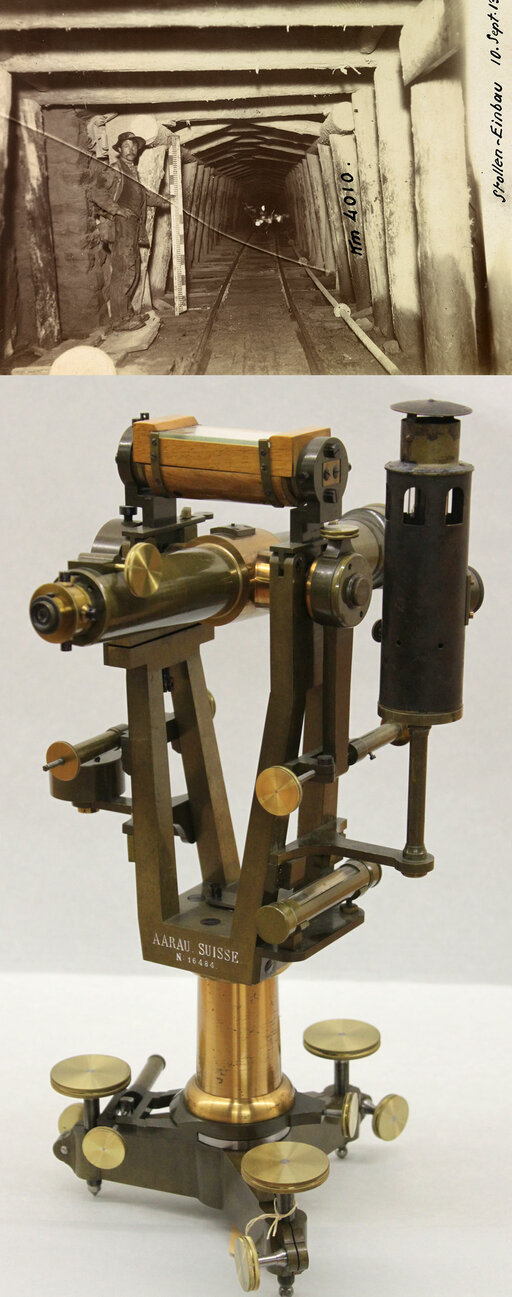

Surveying work for the Simplon Tunnel is carried out using a specially built Kern theodolite
1904
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1904
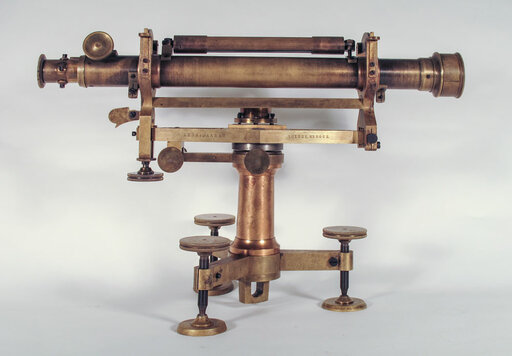
The 1904 model precision level was built based on a report by engineer Heinrich Wild from the department of topography.
1915
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1915

The First World War rages – orders from the Swiss army improve a stagnating business trend.
1920
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1920

Kern moves into a newly built factory in Schachen in Aarau. Among other things, it houses the newly established production of optical systems.
1921
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1921
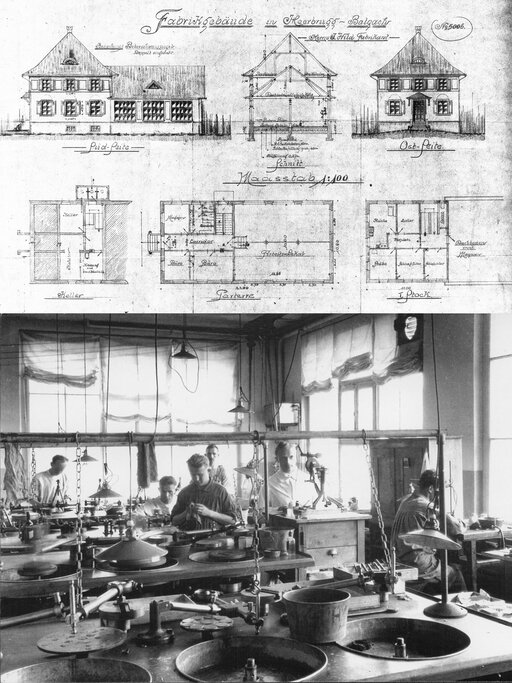
Company «Heinrich Wild, Werkstätte für Feinmechanik und Optik, Heerbrugg» is founded on 26 April 1921.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1921

The production of photographic cameras starts, to be later expanded to include amateur film cameras and stereo cameras.
1923
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1923
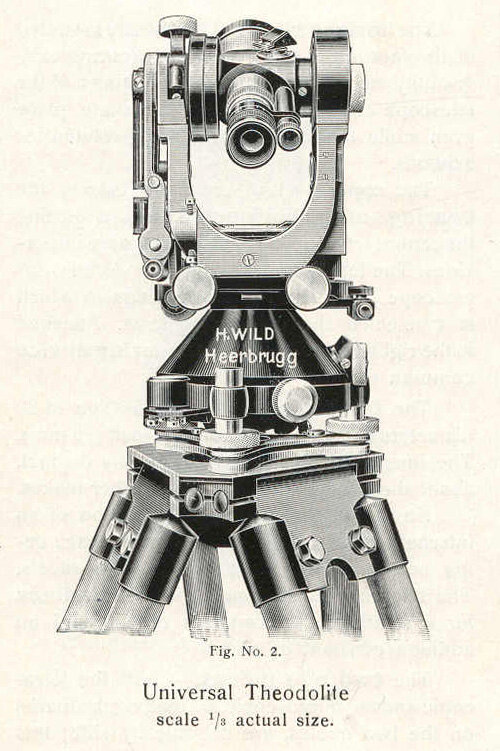
Heinrich Wild revolutionises surveying with the first second theodolite T2.
1924
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1924

The «Heerbrugg factory school» for precision engineers, machine fitters and related professions is founded.
1926
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1926
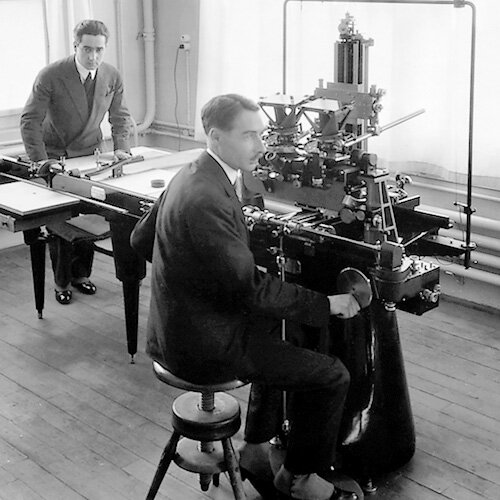

The first two A2 autographs are delivered to the Amt für Landestopografie along with WILD phototheodolites.
1927
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1927

The rapid development of aeroplanes means that aerial cameras can be used. A lens developed by Heinrich Wild himself is used in the new C2 aerial camera.
1929
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1929
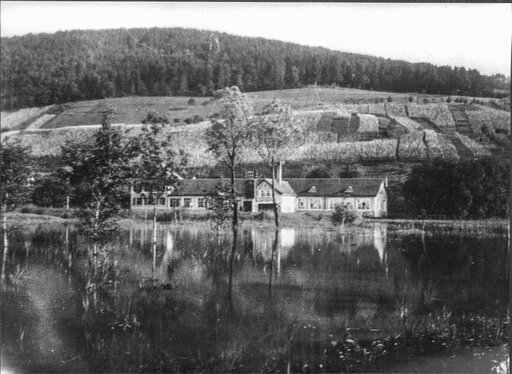
The company WILD generates profits for the first time.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1929

Surveying instruments can now be mass-produced. A welfare foundation and insurance is set up for employees.
1930
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1930
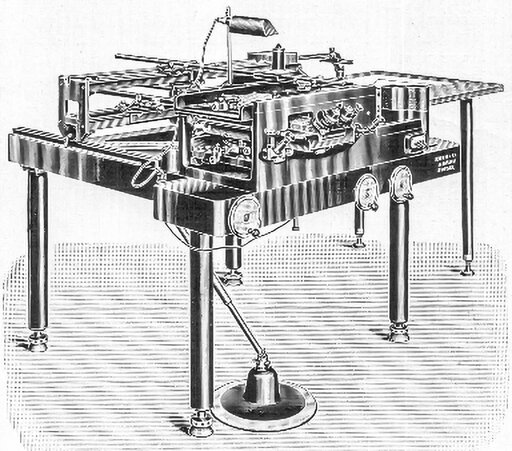
An early autograph is exhibited at the international photogrammetry congress in Zurich.
1932
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1932
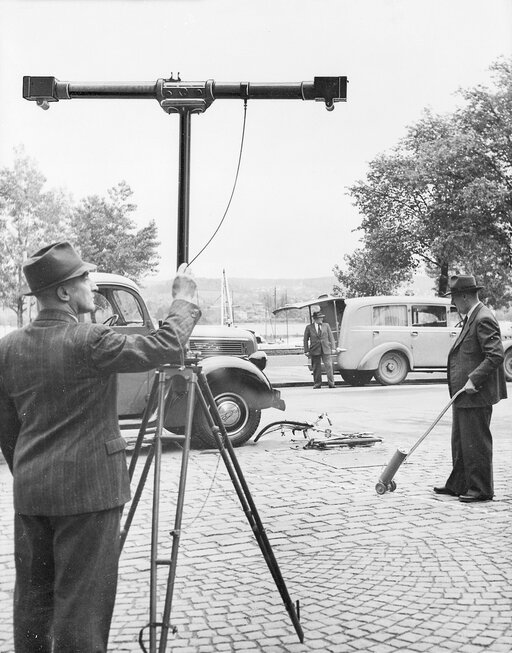

The Wild C12 stereometric camera is launched. It is used for photogrammetric surveying. Countless police organisations around the world used such an instrument for decades.
1933
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1933
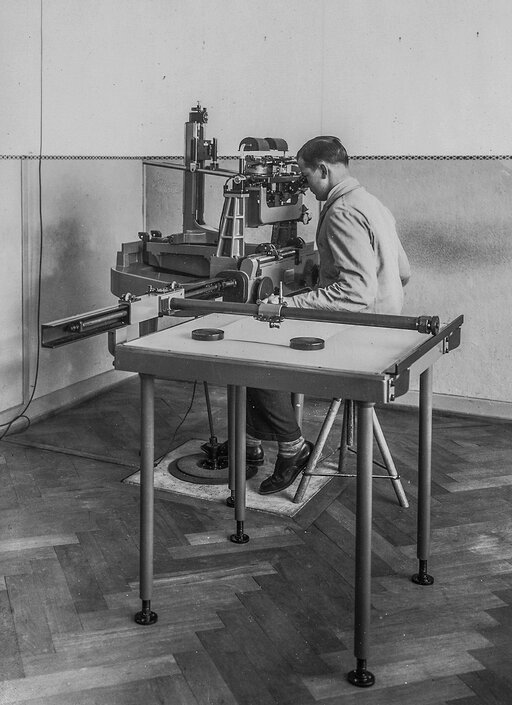

The first WILD A4 autograph is commissioned by the Zurich municipal police in 1933. Devices of this sort are still used in many countries to this day.
1935
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1935

Heinrich Wild signs a contract with Kern & Co. Aarau to develop and manufacture a new range of theodolites.
1939
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1939

The new surveying instruments are displayed at the Swiss national exhibition in Zurich.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1939

The new surveying instruments are displayed at the Swiss national exhibition in Zurich.
1940
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1940

An insurance fund, a precursor to the later pension fund, is set up. A housing office is set up to create low-cost housing for employees.
1942
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1942

Manufacture of drawing sets starts. This was in direct competition with a product range that Kern had been producing since its foundation in 1819.
1943
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1943
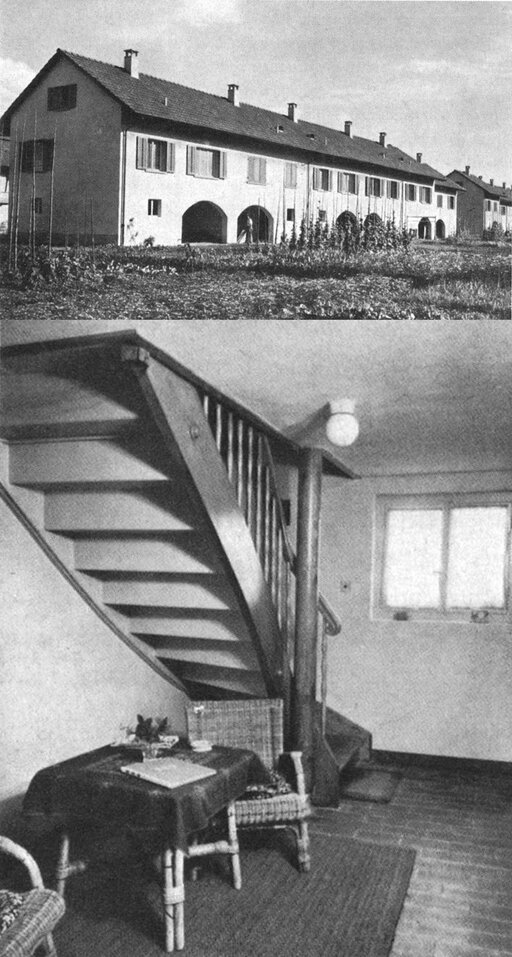

Two residential sites comprising 18 family homes are ready for occupation.
1944
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1944
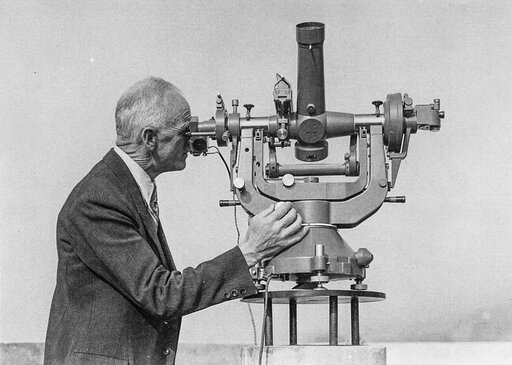
The universal astronomic instrument T4, enabling readings of up to 0.1” (angular seconds) is the pinnacle of mechanical optical precision. The T4 was produced for over four decades and cost 70,000 francs.
1947
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1947
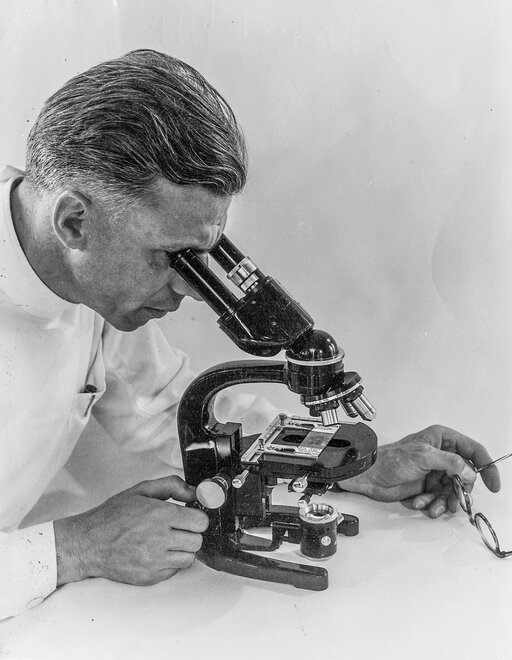

WILD also undertakes pioneering work in the area of microscopy. The first mass-produced research microscopes in Switzerland, types M9 and M10, are launched.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1947
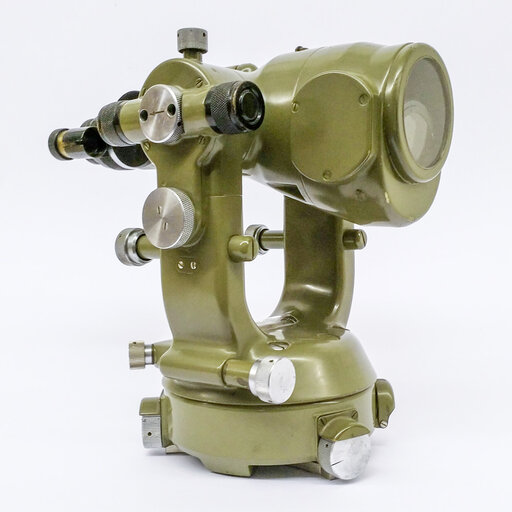

The new double-circle self-reducing tachymeter DK-RT is a standard instrument for land register surveys in Switzerland for decades.
1948
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1948
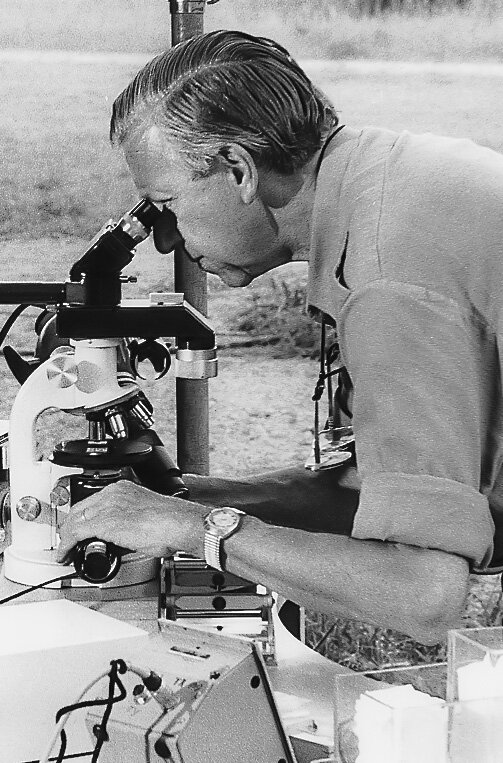
Hans A. Traber managed the development of microscopy from 1948 –1956. He was famous for his nature programmes on Swiss radio and television, broadcast from 1955 onwards.
1959
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1959
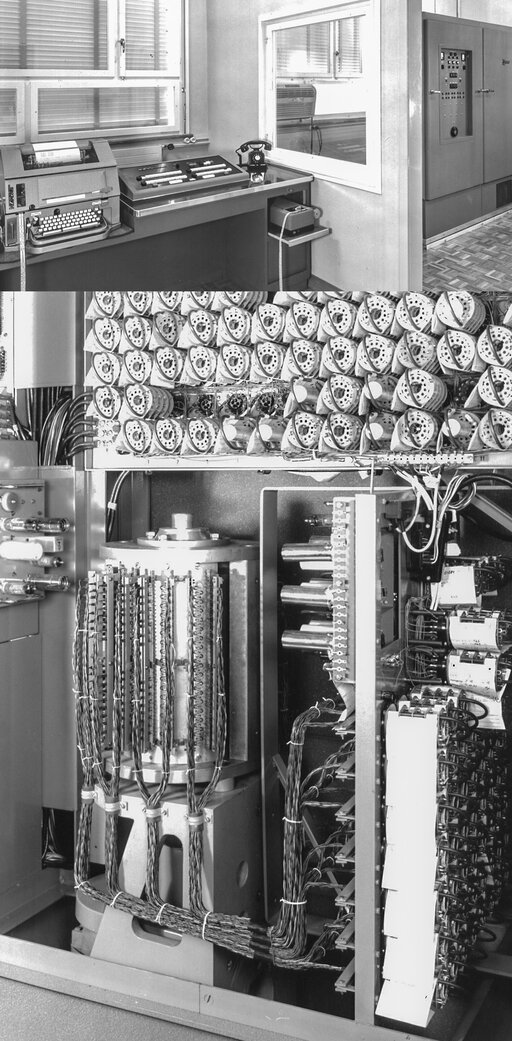
The optical calculation office for scientific tasks receives its first electronic computer, a «Zuse Z22». The first real «computer» owned by an industrial company in Switzerland.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1959
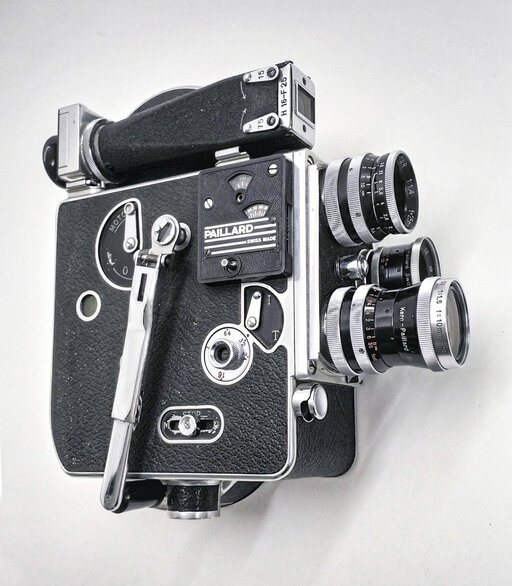

Kern launches the Switar-Objective 1:1,6,f=10 mm with the world's fastest light transmission. This is an important milestone in optics and the stepping stone for the NASA order for the Apollo mission.
1961
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1961

The positive company development continues. On 2 October the 3000th employee joins WILD Heerbrugg AG.
1964
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1964
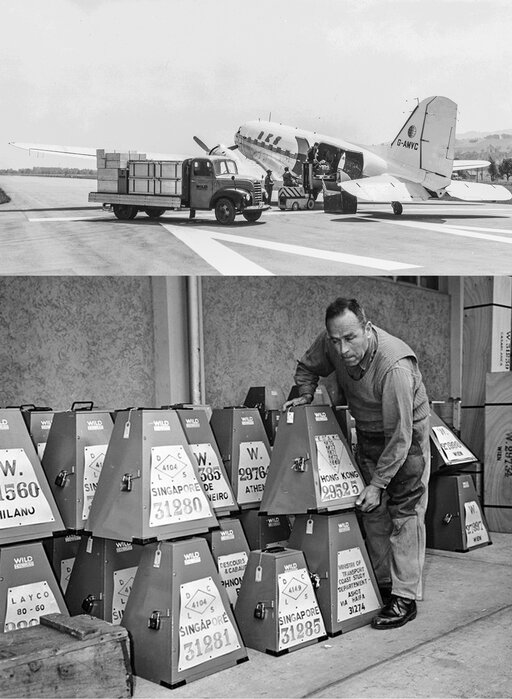

The hundred thousandth WILD theodolite is calibrated in Heerbrugg and shipped off to be used anywhere on planet Earth.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1964
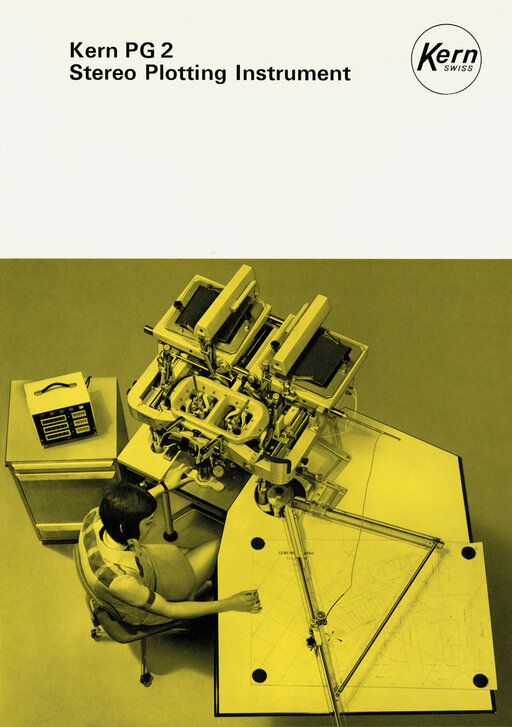
The PG2 plotter marked the breakthrough into modern photogrammetry.
1968
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1968
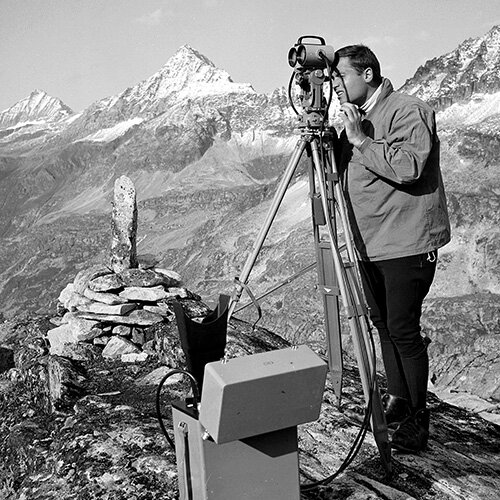

The first infrared distance measurement instrument DISTOMAT DI10 (developed by WILD and French company Sercel) revolutionised surveying technology as the first close range meter. It can measure distances of up to 1000 m with centimetre accuracy.
1969
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1969

«Houston, Tranquility Base here, the Eagle has landed». The first moon landing was filmed with a camera that contained a lens developed and manufactured by Kern.
1970
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1970

Kern revolutionises inclination survey from 1970 wih the «geniale Dose» (eng.: genius box). Today, the liquid compensators are standard with most manufacturers of geodetic industruments.
1971
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1971

At the start of this anniversary year, WILD Heerbrugg employs 4200 employees around the world in manufacturing and sales. A WILD subsidiary is established in the Far East city state of Singapore.
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1971
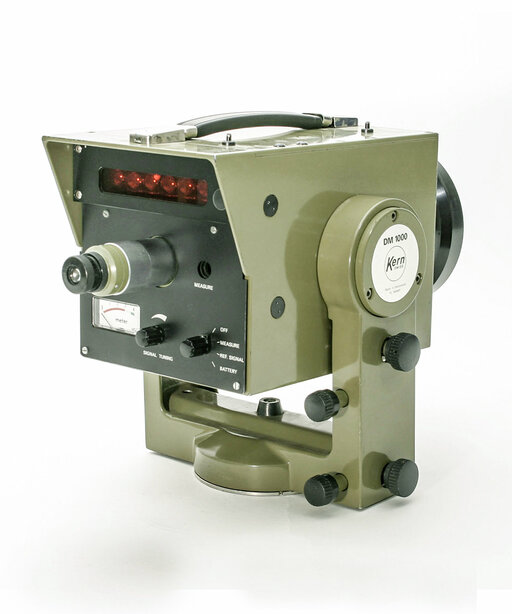

Launch of the first own electronic distance meter DM1000 based on the phase difference method for distances up to 1000 meters. Transmitting and receiving optics are located behind a common lens.
1972
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1972

In September, as part of a capital increase process at Leitz, WILD acquires 25 percent of the share capital in Ernst Leitz GmbH.
1973
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1973

The Kern ME5000 Mekometer is to this day the most accurate laser distance meter. When combined with special software the ME5000 can also be used in close range (> 2 m). Distances of up to 12 km can be surveyed by using special precision reflectors. In 1973 the first generation of mekometers, the ME3000, came onto the market.
1973
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1973

Launch of the then smallest electronic distance meter DM500, which can be plugged onto Theodolite. The DM500 series, consisting of several variants, sold more than 10,000 units in the following years. The transmitting and receiving optics are located behind two separate lenses.
1977
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1977
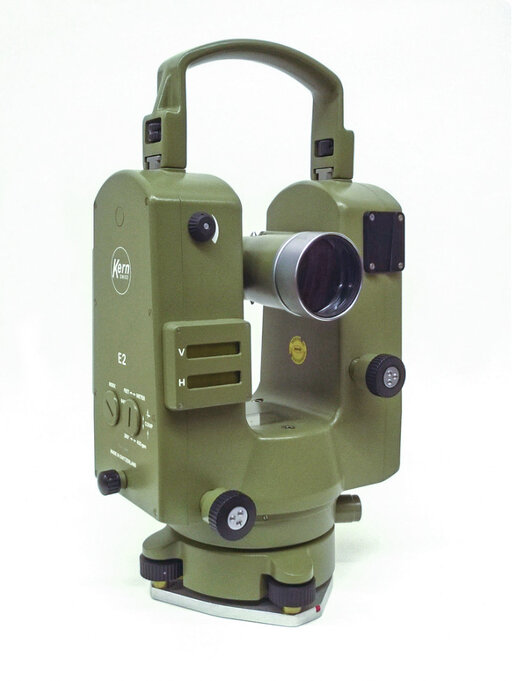

The introduction of electronic theodolites, starting with the Kern E2, is a major step towards digitisation and automation. The in-built liquid compensator formed the basis for the inclination sensors used today.
1978
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1978

The recording electronic self-reducing tachymeter WILD Tachymat TC1 can take care of both measuring the angles and logging the measured values.
1978
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1978
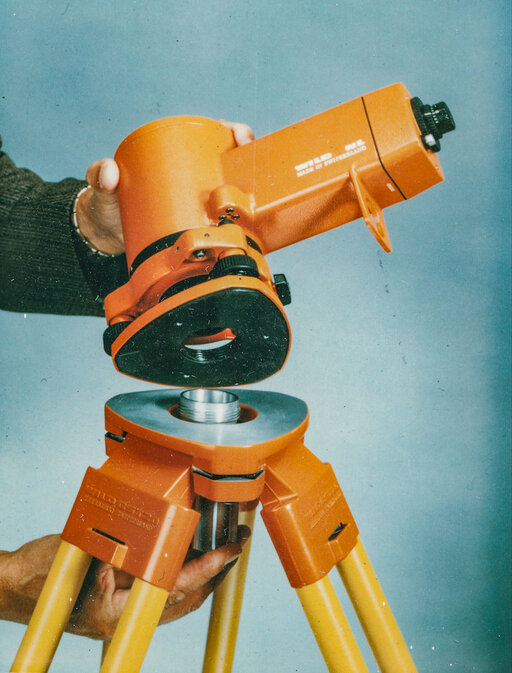

For precision levelling, the geodesy department launches the WILD N3 with an integrated parallel plate micrometer and automatic plummet for both zenith (ZL) and nadir (NL) useful for both high-rise and shaft construction.
1980
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1980

Kern has a breakthrough in analytical photogrammetry with the DSR1 stereoplotter and the GP1 plotter.
1982
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1982
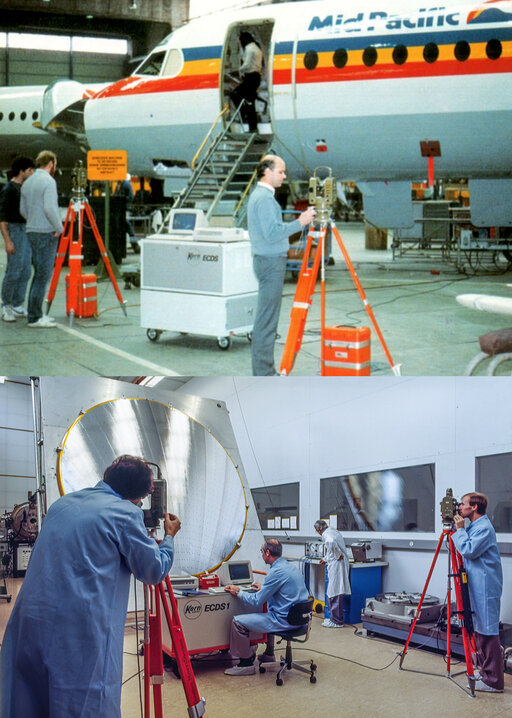

Kern launches the ECDS1 (Electronic Coordinate Determination System) in 1982. The introduction of this electronic theodolite revolutionised traditional industrial surveying and greatly expanded its use.
1983
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1983
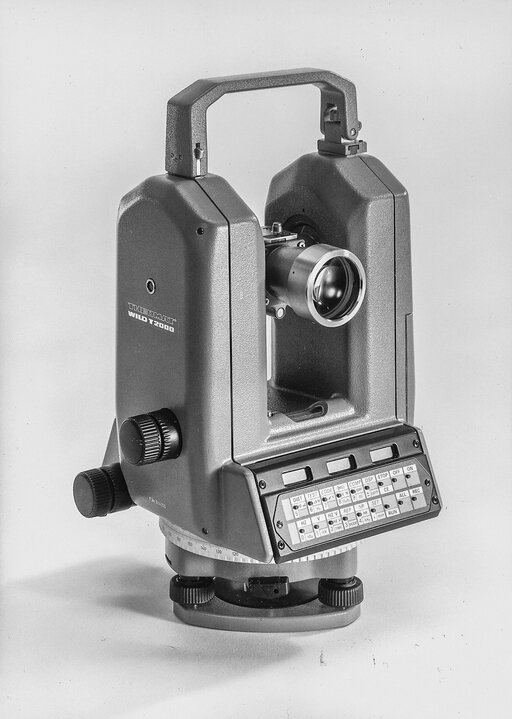

Digitisation starts: 4 March 1983 saw the world premiere of the computerised theodolite, the Theomat WILD T2000, the start of the computer age in surveying technology.
1985
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1985
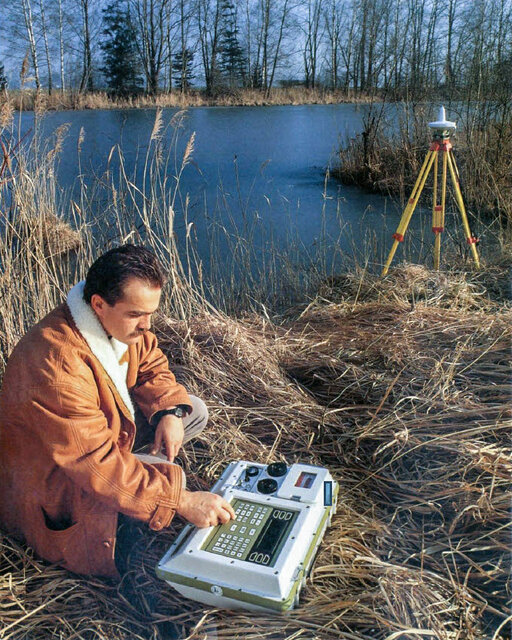

In partnership with American company Magnavox Corporation, the first GPS receiver for surveying applications, the WILD WM101, is launched.
1987
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1987
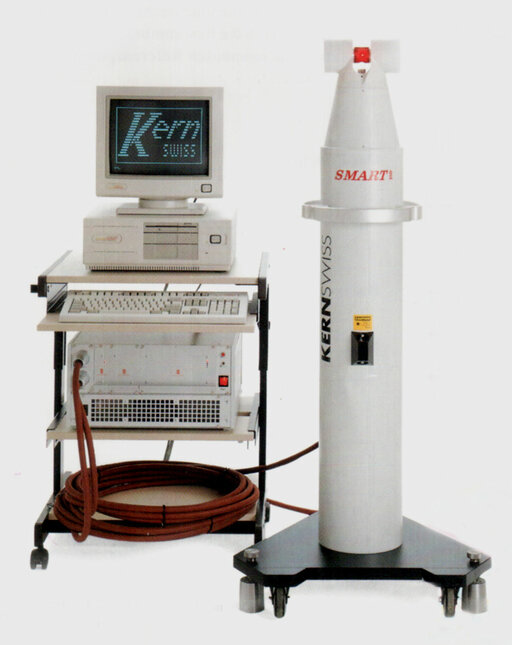

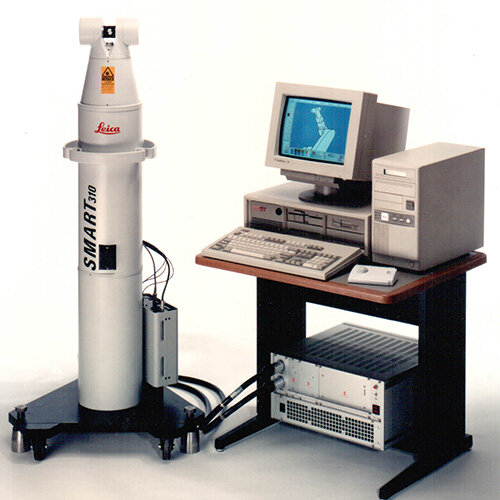
The first prototype of what later became the SMART 310, the first mobile 3D interferometer, is put into service in Detroit. This is the start of the Leica laser tracker success story.
1988
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1988

Kern & Co. AG is taken over by the WILD-Leitz Group.
1988
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
1988

The history of the Kern Study Collection starts in August 1988 with the handover of an extensive collection of historic instruments, documents, films and drawings to the then City Museum Alt-Aarau.
1989
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1989

On 1 January the company WILD Heerbrugg AG is renamed to WILD-Leitz AG, Heerbrugg.
1990
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1990

WILD-Leitz merges with Cambridge Instruments to become the Leica Group.
1991
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1991

Digitisation continues apace: in March the WILD NA2000, the world’s first digital level, causes a sensation at the USA’s most important surveying congress in Denver. It is awarded the photonics innovation prize.
1993
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1993
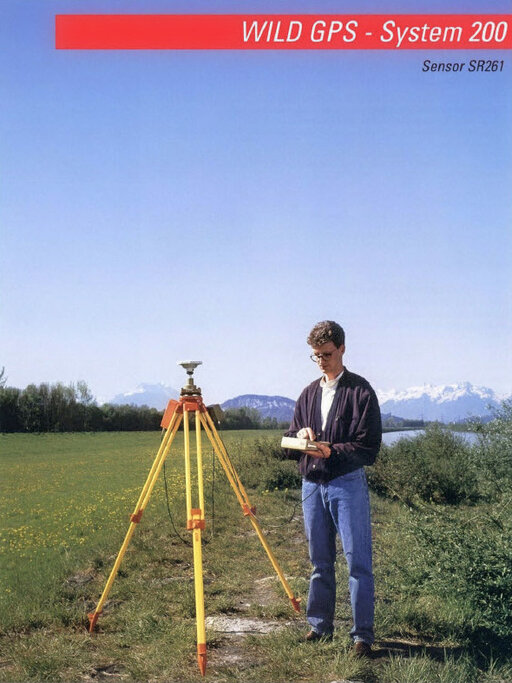

Takeover of the civil GPS division of Magnavox and the introduction of System 200 – the first Leica GPS product.
1993
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1993
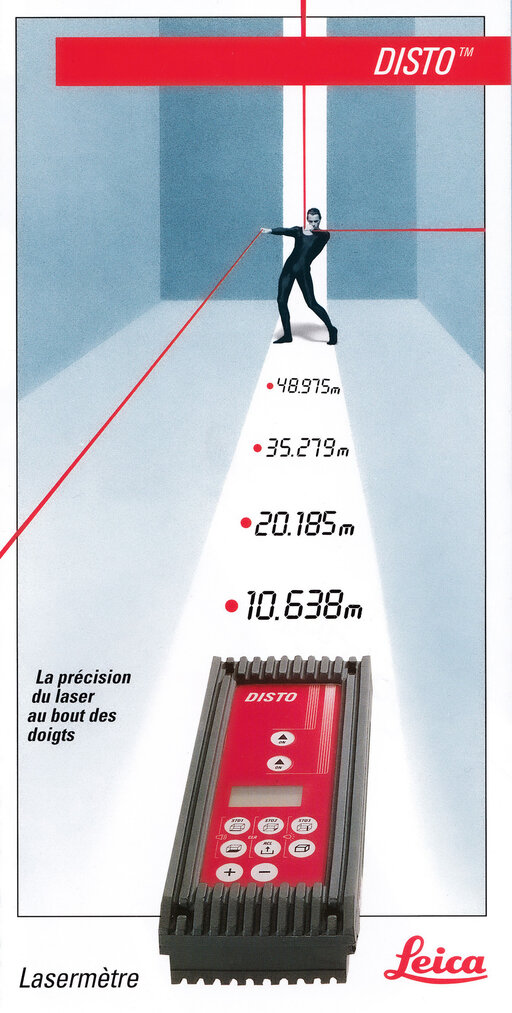
The world's first hand-held laser distance meter, the Leica DISTO, attracts great attention.
1996
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
1996

The Leica Group splits into Leica Microsystems, Leica Geosystems and Leica Camera.
2000
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
2000

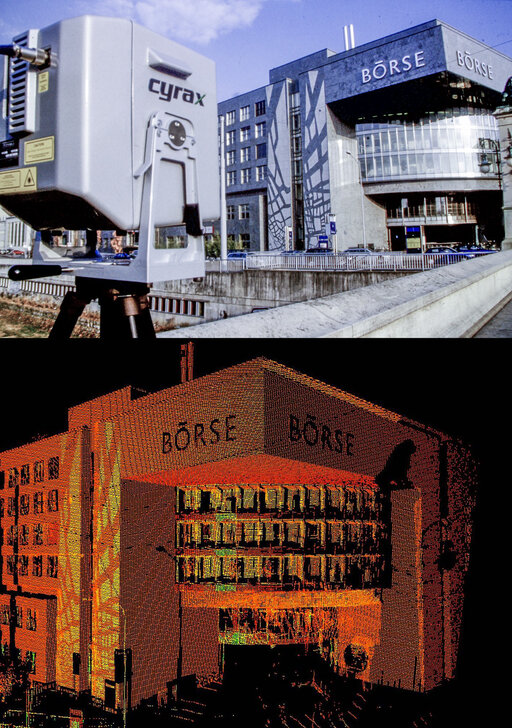
American company Cyra Technologies Inc. is taken over and thus the age of high-definition 3D scanning starts.
2000
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
2000
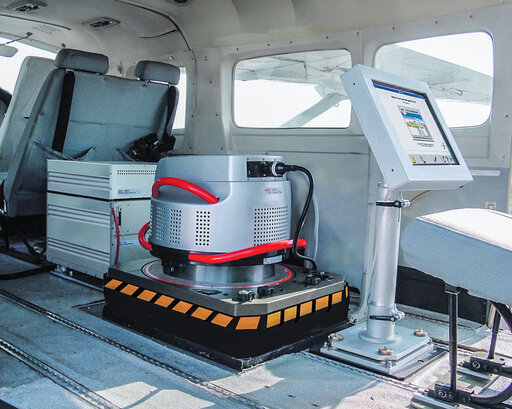

The first digital airborne sensor, ADS40, is presented. A major innovation for the world of photogrammetry.
2005
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
2005

Takeover by Hexagon AB, Sweden, and start of a new era. The innovative power of Kern, Wild and Leica Geosystems still shape Hexagon's world today.
2011
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
2011

A disused civil defence facility at the Aarau City Museum was renovated in 2009 and equipped with the necessary facilities for the reception of visitors. Since May 2011, the Kern Study Collection has been housed in the Aarau City Museum.
2019
WILD Heerbrugg AG Leica Geosystems AG
2019

We celebrate the 200 years anniversary of the founding year of Kern & Co. AG in Aarau as part of «200yrs Swiss Geo x».
2021
Kern & Co. AG Aarau
2021

We celebrate the 100 years anniversary of the founding year of WILD Heerbrugg AG in Heerbrugg as part of «200yrs Swiss Geo x».